|
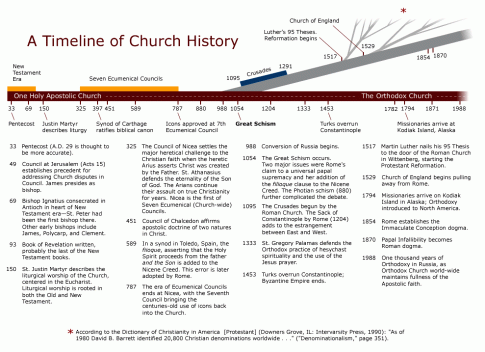
The Orthodox Church was founded by our Lord Jesus Christ and is the living manifestation of His presence in the history of mankind. The most conspicuous characteristics of Orthodoxy are its rich liturgical life and its faithfulness to the apostolic tradition. It is believed by Orthodox Christians that their Church has preserved the tradition and continuity of the ancient Church in its fullness compared to other Christian denominations which have departed from the common tradition of the Church of the first 10 centuries. Today the Orthodox Church numbers approximately 300 million Christians who follow the faith and practices that were defined by the first seven ecumenical councils. The word orthodox ("right belief and right glory") has traditionally been used, in the Greek-speaking Christian world, to designate communities, or individuals, who preserved the true faith (as defined by those councils), as opposed to those who were declared heretical. The official designation of the church in its liturgical and canonical texts is "the Orthodox Catholic Church" (gr. catholicos = universal).
The Orthodox Church is a family of "autocephalous" (self governing) churches, with the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople holding titular or honorary primacy as primus inter pares (the first among equals). The Orthodox Church is not a centralized organization headed by a pontiff. The unity of the Church is rather manifested in common faith and communion in the sacraments and no one but Christ himself is the real head of the Church. The number of autocephalous churches has varied in history. Today there are many: the Church of Constantinople (Istanbul), the Church of Alexandria (Egypt), the Church of Antioch (with headquarters in Damascus, Syria), and the Churches of Jerusalem, Russia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Georgia, Cyprus, Greece, Poland, Czechlands and Slovak, Albania and America In the wider theological sense "Orthodoxy is not merely a type of purely earthly organization which is headed by patriarchs, bishops and priests who hold the ministry in the Church which officially is called "Orthodox." Orthodoxy is the mystical "Body of Christ," the Head of which is Christ Himself (see Eph. 1:22-23 and Col. 1:18, 24 et seq.), and its composition includes not only priests but all who truly believe in Christ, who have entered into the Church He founded, those living upon the earth and those who have died in the Faith and in piety."
The Great Schism between the Eastern and the Western Church (1054) was the culmination of a gradual process of estrangement between the east and west that began in the first centuries of the Christian Era and continued through the Middle Ages. Linguistic and cultural differences, as well as political events, contributed to the estrangement. From the 4th to the 11th century, Constantinople, the center of Eastern Christianity, was also the capital of the Eastern Roman, or Byzantine, Empire, while Rome, after the barbarian invasions, fell under the influence of the Holy Roman Empire of the West, a political rival. In the West theology remained under the influence of St. Augustine of Hippo (354-430) and gradually lost its immediate contact with the rich theological tradition of the Christian East. In the same time the Roman See was almost completely overtaken by Franks.
At the time of the Schism of 1054 between Rome and Constantinople, the membership of the Eastern Orthodox Church was spread throughout the Middle East, the Balkans, and Russia, with its center in Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire, which was also called New Rome. The vicissitudes of history have greatly modified the internal structures of the Orthodox Church, but, even today, the bulk of its members live in the same geographic areas. Missionary expansion toward Asia and emigration toward the West, however, have helped to spread the presence of Orthodoxy worldwide. Today, the Orthodox Church is present almost everywhere in the world and is bearing witness of true, apostolic and patristic tradition to all peoples. The Orthodox Church is well known for its developed monasticism. The uninterrupted monastic tradition of Orthodox Christianity can be traced from the Egyptian desert monasteries of the 3rd and 4th centuries. Soon monasticism had spread all over the Mediterranean basin and Europe: in Palestine, Syria, Cappadocia, Gaul, Ireland, Italy, Greece and Slavic countries. Monasticism has always been a beacon of Orthodoxy and has made and continues to make a strong and lasting impact on Orthodox spirituality. Excerpt taken from The Orthodox Church by Bishop Kallistos (Ware), via orthodoxdelmarva.org.
|
The following articles on Orthodoxy are from the book, These Truths We Hold - The Holy Orthodox Church: Her Life and Teachings, published by and available from Saint Tikhon's Seminary Press:
|